Each ectodermal dysplasia has its own combination of symptoms. Two or more of the key features must function abnormally to be defined as an ectodermal dysplasia. How the key feature is abnormal will vary depending on the syndrome. For example, the hair in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is sparse and fine while it is coarse in ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia-clefting syndrome.
Key Features of Ectodermal Dysplasias
When considering an ectodermal dysplasia diagnosis, a physician and dentist would first evaluate the following five parts of the body for abnormalities.
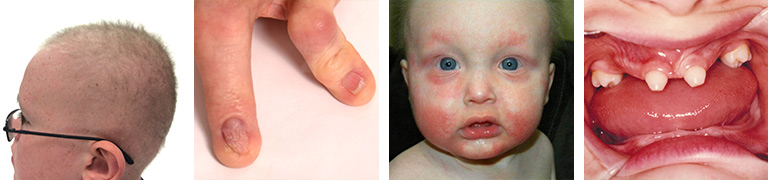
- Hair may be missing, sparse or very light in color. Read more detailed information about hair symptoms in ectodermal dysplasias.
- Nails may be thick or thin, abnormally shaped or ridged. Read more detailed information about nail abnormalities in ectodermal dysplasias.
- Skin may be thin, dry, and prone to rash, infection and sunburn. Read more detailed information about skin symptoms in ectodermal dysplasias.
- Sweat glands may not work properly or may not have developed at all, leaving people unable to perspire and at risk for overheating. Read more detailed information about the inability to sweat in ectodermal dysplasias.
- Teeth may be missing, pointed or widely spaced. Read more detailed information about dental symptoms in ectodermal dysplasias.
Other Body Parts That Can Be Affected
- Ears may have ear wax impaction, which can cause hearing loss and hearing nerve damage.
- Eyes may lack tears, have blepharitis or corneal scarring, or be sensitive to light.
- Limbs may be missing fingers and toes or have fused fingers and toes.
- Noses may have a thick mucus secretion (“nasal rocks”) or foul smelling secretions.
- Throats may have sparse saliva, causing problems with tasting, lubricating, chewing and swallowing foods.
Ectodermal Dysplasia Can Also Cause the Following Medical Issues:
- Cleft lip and palate
- Allergies and immunodeficiencies, such as increased frequencies of asthma, allergies, eczema or rhinitis symptoms
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as constipation
- Growth issues, such as small stature, failure to thrive, prominent forehead, saddle nose, decreased breast development in females, and height and weight deficits beginning at an early age and persisting throughout adolescence
- Obstetrics and gynecology issues, such as a lack of breast development, infertility and breastfeeding complications
- Respiratory system issues, such as recurring respiratory infections
Identifying the symptoms you or your loved one has is the first step. Identifying treatment options is the second.